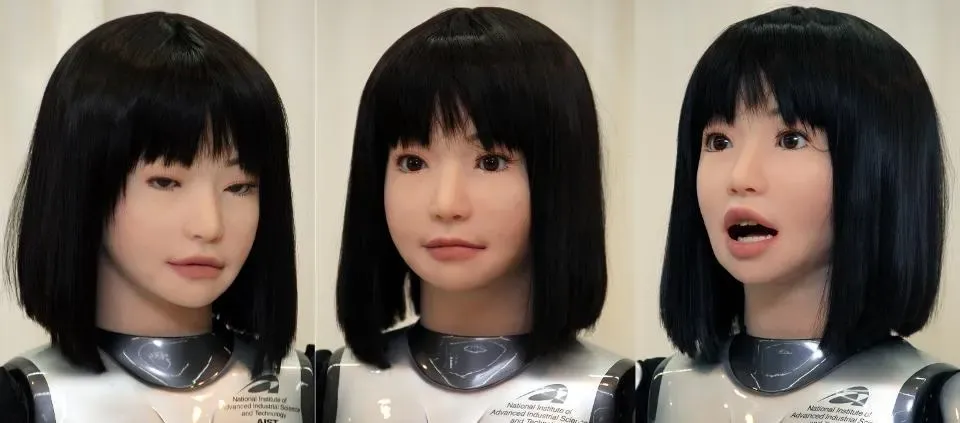
Conceptualization and Design
The first step in creating realistic human-like robots is conceptualization and design. Here, you need to develop a clear idea of what the robot should achieve and its primary features. Do you want it to assist in everyday tasks, or perhaps serve in a healthcare environment? Understanding these objectives is crucial as they guide all subsequent decisions in the design process. Moreover, laying out essential features can help prioritize which aspects of functionality are most important. It is vital to keep in mind the growing field of Human Like Robots as a benchmark for innovation and capabilities.
Performing market research and analysis is an essential part of this phase. You must identify what already exists in the market and assess potential competitors. Is there already a robot that fulfills your intended purpose? Analyzing market needs can help you pinpoint gaps or opportunities for innovation. Engaging directly with potential users through surveys or interviews can provide invaluable feedback, ensuring your design meets real-world needs. It’s also important to study trends and potential future demands to ensure longevity in your project.
Once you've gathered the necessary data, you can turn to sketching and 3D modeling. This is where creativity meets technology. Start with rough sketches to visualize ideas before moving to more detailed 3D models using computer-aided design (CAD) software. These models allow for adjustments and improvements before any physical concept is produced. Moreover, they make it easier to communicate ideas with team members and stakeholders. Creating virtual prototypes can also help in visualizing how the robot will perform in varied tasks and environments.
Materials and Technologies
The choice of advanced materials is crucial for building robots that are both functional and appealing. Lightweight yet durable materials like carbon fiber and advanced polymers can enhance mobility and performance. They can withstand wear and tear while also allowing for intricate designs that mimic human features. Additionally, selecting materials that can endure various climates and conditions increases the robot's usability. Incorporating recyclable or biodegradable materials can also position your robot as a more environmentally friendly option in the market.
Incorporating soft robotics is becoming increasingly popular in creating more adaptable and safe human-like robots. Soft robotics employs materials that allow robots to adapt to their surroundings, making them safer for everyday interactions with humans. This technology can mimic the flexibility of human muscles and skin, providing a more relatable appearance. It also allows for softer movements, reducing the potential for injury during interactions. As technology progresses, integrating soft materials into robot design is likely to create even more life-like movements.
Integration of sensors and actuators is a pivotal step in ensuring the robot can interact with its environment effectively. Sensors help the robot understand its surroundings by detecting things like distance, temperature, and motion. Meanwhile, actuators are responsible for the robot's movements, mimicking muscles and joints. Together, these elements create a system that allows for informed decision-making and effective responses to external stimuli. An optimal combination of sensors and actuators can lead to a robot capable of nuanced interactions, making it appear more human-like in behavior.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Developing natural language processing (NLP) algorithms is essential for building robots that can communicate with humans. This technology allows robots to understand and respond to spoken language, making interactions feel more organic. They can interpret commands and engage in conversations by analyzing context. As consumer expectations for technology rise, the demand for advanced NLP capabilities increases. Ensuring your robot can understand various languages and dialects can broaden its user base and market appeal.
Building adaptive behavioral models is another critical aspect of artificial intelligence in robotics. These models allow robots to learn from their interactions, adjusting their responses based on user behavior. By using machine learning algorithms, they can refine their performance over time. This adaptability enhances the robot's ability to serve unique user needs, making it more effective in diverse situations. As a result, the robot can become a more trusted companion or assistant, as it learns to predict user preferences.
Implementing computer vision systems plays a crucial role in enriching the robot's understanding of the world. Vision systems equip robots with the ability to see and interpret visual data, mimicking human sight. This technology enables the robot to recognize people, objects, and even gestures. By combining computer vision with NLP, robots can engage in richer interactions, responding to visual cues in human communication. As this technology evolves, it leads to more intuitive and dynamic robot behavior, enhancing user experiences.
Mechanical and Electrical Engineering
The design of joint and limb mechanics is foundational for ensuring a robot's flexibility and movement resemble that of a human. Engineers must create joints that allow for a wide range of motion while maintaining stability. This includes designing mechanisms that replicate the natural movement of human joints, such as ball-and-socket and hinge joints. The development process often includes prototyping and testing to identify potential issues with range and strength. The goal is to create robots that can move smoothly and naturally, making interactions more comfortable for users.
Efficient power supply and management systems are also paramount in robotic design. The robot must have a reliable energy source to operate effectively during its intended tasks. This could involve developing rechargeable battery systems or even exploring alternative energy sources. Achieving a balance between power consumption and performance can be challenging. Smart energy management systems can help extend the robot's operational time and ensure there's enough power for various tasks.
Lastly, circuit design and microcontroller integration are crucial in connecting all electronic components within the robot. A well-designed circuit allows different parts of the robot to communicate effectively. Engineers need to ensure that microcontrollers can work seamlessly with software, sensors, and actuators. This integration is vital for the robot's success, as any failure in communication can disrupt the entire system. Proper testing during this phase ensures that the circuitry supports efficient robot functionality.
Software Development
Programming core functionalities is where the robot's capabilities come to life. A competent software framework allows the robot to process information, learn behaviors, and perform tasks. This involves writing code that integrates AI algorithms, sensory data, and mechanical operations. Well-structured code can facilitate updates and improvements over time, preventing obsolescence. Thorough testing during this phase is critical to diagnosing bugs and ensuring reliability.
Creating user interaction interfaces is also important for ensuring a positive experience. This means designing software that allows users to engage with the robot intuitively. Whether through a touch screen, app, or voice command, the interface should be user-friendly. Users should easily access available features and receive clear feedback, enhancing their interaction quality. Simplifying user experiences promotes customer satisfaction and trust in the technology.
Lastly, addressing software safety and security is essential. In an age where data breaches are common, ensuring that your robot can protect user information is vital. Strong security measures must be integrated into the software to prevent unauthorized access. Regular updates can help in maintaining security as new threats emerge. Robust safety protocols reassure users, fostering confidence in the robot's functionality and protecting sensitive information.
Testing and Iteration
Prototype testing and evaluation form a critical part of the development process. It’s during this phase that you check how well your robot performs in real-world scenarios. Creating several prototypes allows for multiple rounds of testing. Observing how the robot interacts with its environment can reveal flaws or areas for improvement. Feedback from these evaluations can guide necessary modifications, ensuring the final product meets expectations.
Analyzing user feedback for improvements is another step in refining the design. Engaging potential users early in the process can yield insightful perspectives. This could involve focus groups or pilot programs where users interact with the robot in trial phases. Taking their feedback into account ensures that the robot is more likely to fulfill actual user needs. Continuous engagement helps foster a connection between developers and users, which can be instrumental in long-term success.
Troubleshooting and debugging are the final touches that ensure a smooth operation. These processes involve identifying and fixing any issues that arise in the software or hardware. Engineers must methodically address errors to prevent future problems. A focus on thorough debugging during iterations can help reduce the likelihood of significant failures in the future. Ensuring a reliable outcome goes a long way in boosting the robot's credibility and effectiveness.
Ethical Considerations and Compliance
While creating human-like robots, it’s fundamental to address privacy concerns. As robots often require vast amounts of personal data to function effectively, protecting this information is vital. Transparency about data usage is essential to foster trust with users. Implementing strong privacy policies helps ensure that users feel secure using the technology. This move can also safeguard your project from potential legal issues down the road.
In addition, ensuring ethical AI implementation is increasingly important in robotics. Developers need to establish guidelines that reinforce fairness and prevent bias in algorithms. Inadequate attention to ethics can lead to unintended consequences in robot behavior. Developers should regularly review and revise ethical guidelines to reflect changing societal norms and concerns. Addressing ethics upfront can aid in creating a socially responsible product.
Finally, compliance with legal and safety standards is a critical requirement for any robotics project. Adhering to these standards helps in preventing legal disputes and ensures public safety. Regulations may vary based on location, so it’s crucial to stay informed about local laws. Compliant robots are more likely to gain acceptance in various markets. Ensuring safety standards are met can be a significant asset in marketing the final product.
Production and Deployment
Scaling production processes is an important phase once the design and testing are complete. When a design is finally approved, it’s time to consider how to mass-produce the robots efficiently. This requires extensive planning and coordination with manufacturers. Utilizing advanced manufacturing techniques can lead to cost reductions and increased efficiency. Smooth scaling ensures that you can meet demand without compromising quality.
Establishing quality assurance protocols is critical for maintaining high standards throughout the manufacturing process. These protocols involve checking each robot for functionality and safety before it leaves the production line. A systematic approach to quality ensures consistent performance across all units. Implementing regular audits can help identify areas for improvement in production. Maintaining quality helps build a good reputation in the marketplace.
Lastly, developing strategies for market introduction and support is essential for the success of new robots. This includes planning promotional campaigns to increase visibility. Considering partnerships with businesses that can benefit from your robot can also expand your reach. Ongoing support, including customer service and updates, encourages long-term user engagement. A well-planned market entry can set the stage for successful adoption and continued growth.
Future Trends and Innovations
The advances in AI capabilities continue to shape the future of human-like robots. As AI technology evolves, robots will increasingly be able to understand complex human emotions and social cues. This progression allows robots to engage in deeper, more meaningful interactions. Enhanced conversational skills can help robots serve in areas like therapy, education, or companion services. The next generation of robots might even possess the ability to learn from emotional contexts, pushing boundaries further.
Exploring sustainable and eco-friendly materials in robot construction is gaining momentum. As society becomes more environmentally conscious, using recyclable materials can enhance the appeal of robotic products. Innovations in bio-materials are also making it easier to create durable yet sustainable robots. By prioritizing green manufacturing processes, developers can reduce their carbon footprint. This shift can also capture the interest of eco-aware consumers, potentially boosting market demand.
Lastly, the prospects for collaboration with bioengineering for enhanced realism are vast. By studying biological systems and models, engineers can create robots that mimic human behavior even more closely. Integrating discoveries from fields such as neurobiology can lead to advancements in robot cognition. Enhanced realism can also improve user interactions, making robots feel more like part of the human experience. Future collaborations may pave the way for groundbreaking advancements, pushing human-like robots beyond current limitations.